Incredible detail.
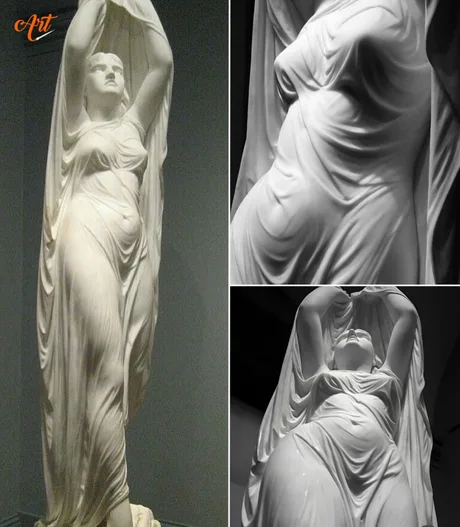
Undine Rising from the Fountain by Chauncey Bradley Ives, a romantic marble sculpture of the water spirit emerging from the waves. Created in 1884, it resides in the Yale University Art Gallery.
#Awesome
Read More...

Prediction completed successfully, lmao '-' future prediction done
Back in 1975 'The muppet Show predicted what most women would look like in 2024 #TheMuppetShow Read More...