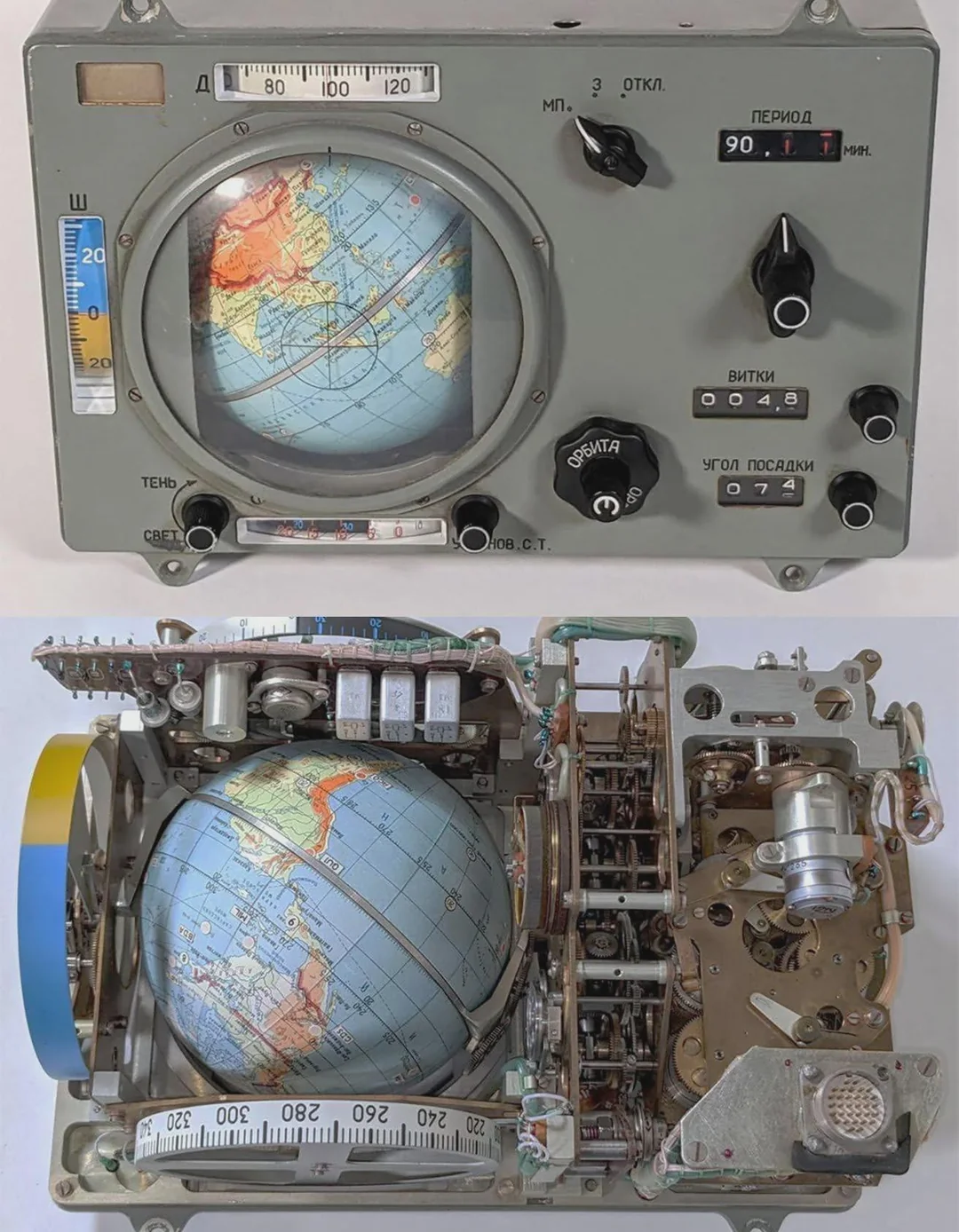
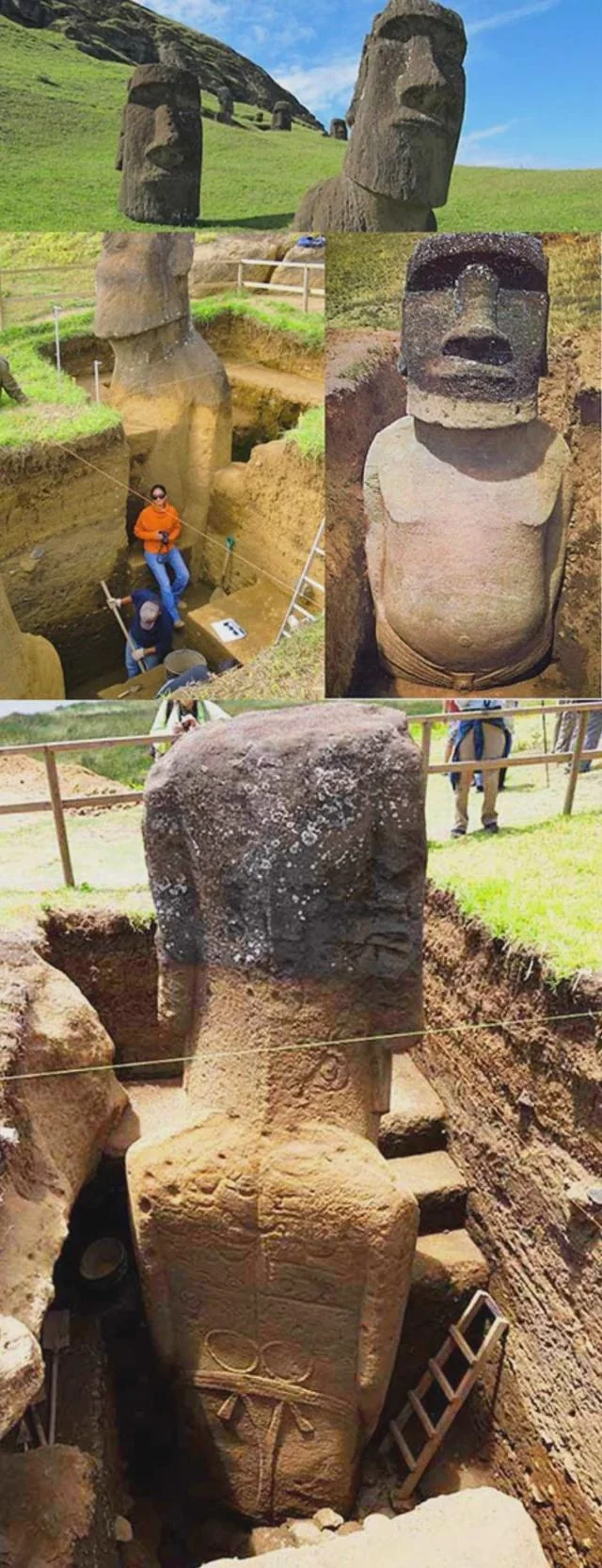
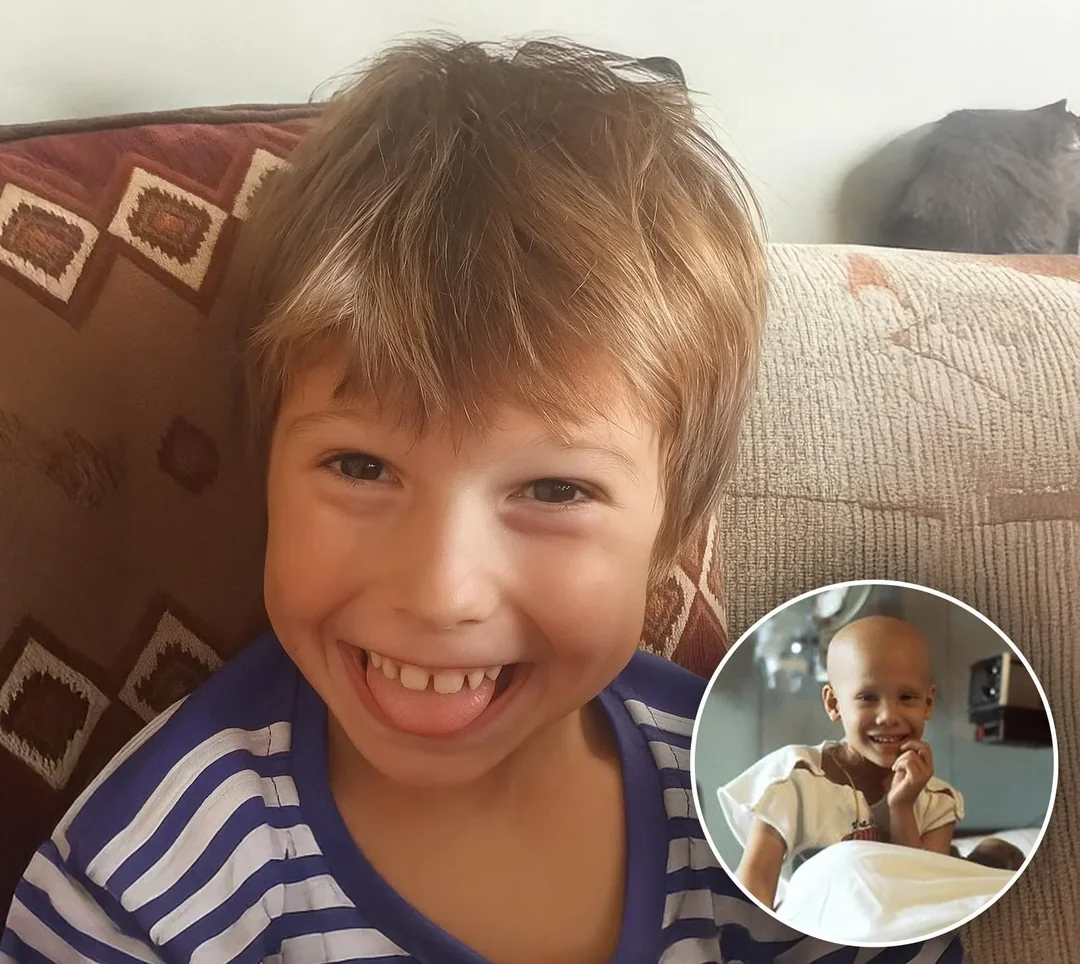
⚔️✨ Warriors of the Pharaoh ✨⚔️
This powerful relief shows the Pharaoh in a dynamic pose, striking down his enemy, symbolizing his strength and dominance in battle. 🏺 The scene illustrates the Pharaoh’s role as both a ruler and warrior, defending Egypt and maintaining order through military might.
Such depictions were common in ancient Egyptian art, designed to showcase the Pharaoh's divine authority and ability to protect the land from invaders. 🌍 These carvings serve as reminders of the Pharaoh’s role as protector of Egypt, as well as their divine connection to the gods. 🌟
#AncientEgypt #Pharaoh
#EgyptianArt #WarriorKing #EgyptianHistory #DivineAuthority
#BattleScenes #ProtectorsOfEgypt
#PharaohPower #HistoricalRelief #AncientCivilizations #EgyptianCulture
Read More...
 GIF
GIF
The Evolution of Humanity
The story of human evolution is a fascinating journey that spans millions of years, detailing the transformation of early primates into modern humans. This evolutionary path is marked by significant milestones in physical, cognitive, and cultural development.
Early Beginnings
The journey of human evolution begins with our ancient primate ancestors. Around 7 million years ago, the first hominins, the group that includes modern humans and our closest relatives, diverged from the ancestors of chimpanzees and bonobos. These early hominins, such as Sahelanthropus tchadensis, had both ape-like and human-like characteristics.
The Australopithecines
One of the most well-known early hominins is Australopithecus afarensis, exemplified by the famous fossil "Lucy," discovered in Ethiopia. Living around 3.9 to 2.9 million years ago, Australopithecus afarensis walked upright on two legs, a crucial step in human evolution, while still retaining some tree-climbing adaptations.
The Genus Homo
Around 2.4 million years ago, the genus Homo emerged. Homo habilis, known as the "handy man," was one of the earliest members of this genus. Homo habilis is associated with the creation of simple stone tools, marking the beginning of technological innovation.
Homo Erectus and Migration
Homo erectus, appearing around 1.9 million years ago, was a significant step forward in human evolution. This species exhibited larger brain sizes and more advanced tool use. Homo erectus was also the first hominin to migrate out of Africa, spreading to Asia and Europe, showcasing adaptability and survival skills in diverse environments.
Neanderthals and Modern Humans
One of the most famous relatives of modern humans is the Neanderthal (Homo neanderthalensis), who lived in Europe and western Asia. Neanderthals were skilled hunters and toolmakers, and they even created symbolic art and buried their dead. Around 300,000 years ago, Homo sapiens, our own species, emerged in Africa. Homo sapiens exhibited advanced cognitive abilities, leading to sophisticated language, art, and cultural practices.
The Great Leap Forward
Approximately 70,000 years ago, Homo sapiens underwent a "Great Leap Forward," marked by a significant increase in creativity and technological innovation. This period saw the development of complex tools, art, and the beginnings of organized societies.
The Agricultural Revolution
About 10,000 years ago, the Agricultural Revolution transformed human societies. The domestication of plants and animals led to the development of agriculture, allowing humans to settle in one place and form complex civilizations. This period saw the rise of cities, writing systems, and advanced technologies.
Modern Humans
Today, Homo sapiens are the only surviving members of the hominin lineage. Our species has spread across the globe, adapting to various environments and developing diverse cultures. The study of human evolution continues to uncover new insights, helping us understand our origins and the traits that make us uniquely human.
The journey of human evolution is a testament to the resilience, adaptability, and ingenuity of our ancestors. It highlights the incredible transformations that have shaped us into the complex beings we are today.
Read More...

The History of Space Exploration
Space exploration is one of humanity's most significant achievements, showcasing our desire to explore the unknown and push the boundaries of what is possible. From the earliest rocket experiments to landing on the Moon and exploring distant planets, the journey of space exploration has been marked by remarkable milestones and technological advancements.
Early Beginnings
The dream of space travel dates back centuries, with early theories and stories about flying to the stars. However, practical attempts began in the early 20th century with the development of rocketry. Pioneers like Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, Robert Goddard, and Hermann Oberth laid the groundwork for modern rocketry with their theories and experiments.
The Space Race
The Cold War era saw the rise of the Space Race between the United States and the Soviet Union, driving rapid advancements in space technology. On October 4, 1957, the Soviet Union launched Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite, marking the beginning of the Space Age. This achievement spurred the United States to accelerate its space program.
Human Spaceflight
The next significant milestone was human spaceflight. On April 12, 1961, Yuri Gagarin, a Soviet cosmonaut, became the first human to orbit the Earth aboard Vostok 1. This historic flight demonstrated the feasibility of human space travel and intensified the Space Race.
The Moon Landing
One of the most iconic achievements in space exploration is the Apollo 11 mission. On July 20, 1969, NASA's Apollo 11 mission successfully landed astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin on the Moon, while Michael Collins orbited above. Armstrong's famous words, "That's one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind," echoed around the world as he became the first human to set foot on the lunar surface.
Space Stations
The development of space stations allowed humans to live and work in space for extended periods. The Soviet Union launched the first space station, Salyut 1, in 1971. Later, the International Space Station (ISS), a collaborative effort involving multiple countries, became a symbol of international cooperation in space exploration. The ISS has been continuously occupied since November 2000, conducting scientific research and technological experiments.
Mars Exploration
Mars has been a focal point of robotic exploration. NASA's Viking program, launched in the 1970s, sent two landers to Mars, providing valuable data about the Martian surface and atmosphere. More recently, rovers like Spirit, Opportunity, Curiosity, and Perseverance have explored Mars, searching for signs of past life and studying the planet's geology and climate.
The Future of Space Exploration
The future of space exploration holds exciting possibilities. Space agencies and private companies are working on missions to return humans to the Moon, establish a sustainable presence on Mars, and explore asteroids and other celestial bodies. Innovations in spacecraft design, propulsion systems, and international collaborations are paving the way for the next era of space exploration.
Space exploration continues to inspire and drive technological advancements, expanding our understanding of the universe and our place within it. As we look to the stars, the spirit of exploration and discovery that has guided humanity for centuries will undoubtedly lead us to new frontiers and unimaginable achievements.
Read More...

The Importance of History for Humanity
History, often viewed as a collection of past events, holds far more significance than merely recording what has happened. It is the bedrock of human civilization, shaping our present and influencing our future. The study of history is crucial for several reasons, each highlighting its profound impact on humanity.
Understanding Human Nature
History provides insights into human behavior and societal development. By studying the actions, motivations, and outcomes of people in different eras, we can better understand what drives human behavior. This knowledge helps us predict how societies might react to current and future events, fostering empathy and cultural awareness.
Learning from the Past
One of the most significant benefits of studying history is learning from past mistakes and successes. Historical events, whether triumphs or tragedies, offer valuable lessons. For example, understanding the causes and consequences of wars, economic collapses, and social movements can guide current leaders in making informed decisions to avoid repeating errors.
Cultural Identity and Heritage
History is a vital component of cultural identity. It helps individuals and communities understand their roots, traditions, and shared values. This sense of belonging and continuity fosters unity and pride among people. Preserving historical landmarks, documents, and artifacts allows future generations to connect with their heritage and maintain a sense of identity.
Building Critical Thinking Skills
The study of history involves analyzing sources, understanding context, and interpreting different perspectives. This process develops critical thinking and analytical skills. Historians must evaluate evidence, identify biases, and construct coherent narratives. These skills are transferable to various fields, enhancing problem-solving abilities and informed decision-making.
Shaping the Future
History is not just about the past; it actively shapes the future. By understanding historical trends and patterns, we can anticipate potential challenges and opportunities. History informs policy-making, education, and innovation. For instance, lessons learned from historical pandemics have guided modern public health responses to crises like COVID-19.
Preserving Human Achievements
History chronicles human achievements and milestones, celebrating progress in science, art, literature, and philosophy. Recognizing these accomplishments inspires future generations to strive for excellence and contribute to the collective knowledge and advancement of humanity.
Promoting Social Justice
Studying history highlights the struggles for freedom, equality, and justice. It brings attention to the marginalized and oppressed, ensuring their stories are not forgotten. This awareness promotes social justice and encourages efforts to create a more equitable and inclusive society.
In conclusion, the importance of history for humanity cannot be overstated. It is a treasure trove of knowledge that informs our understanding of human nature, guides decision-making, preserves cultural identity, builds critical thinking skills, shapes the future, celebrates achievements, and promotes social justice. Embracing history enables us to learn from the past, navigate the present, and build a better future.
Follow for more @HistoryEchoes
Read More...