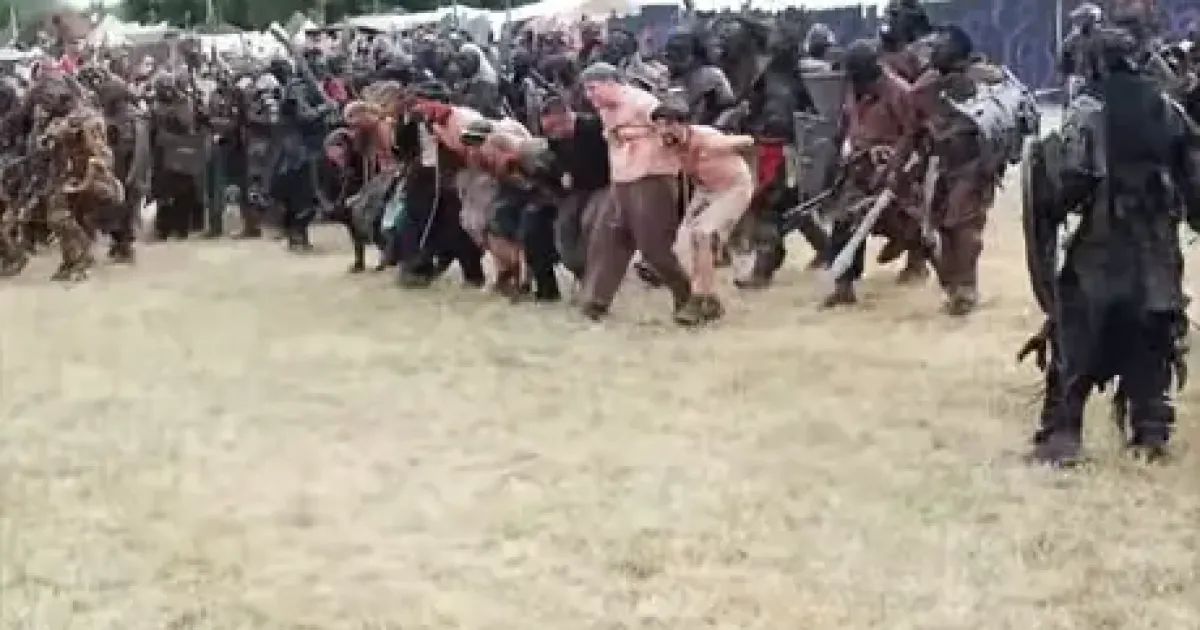
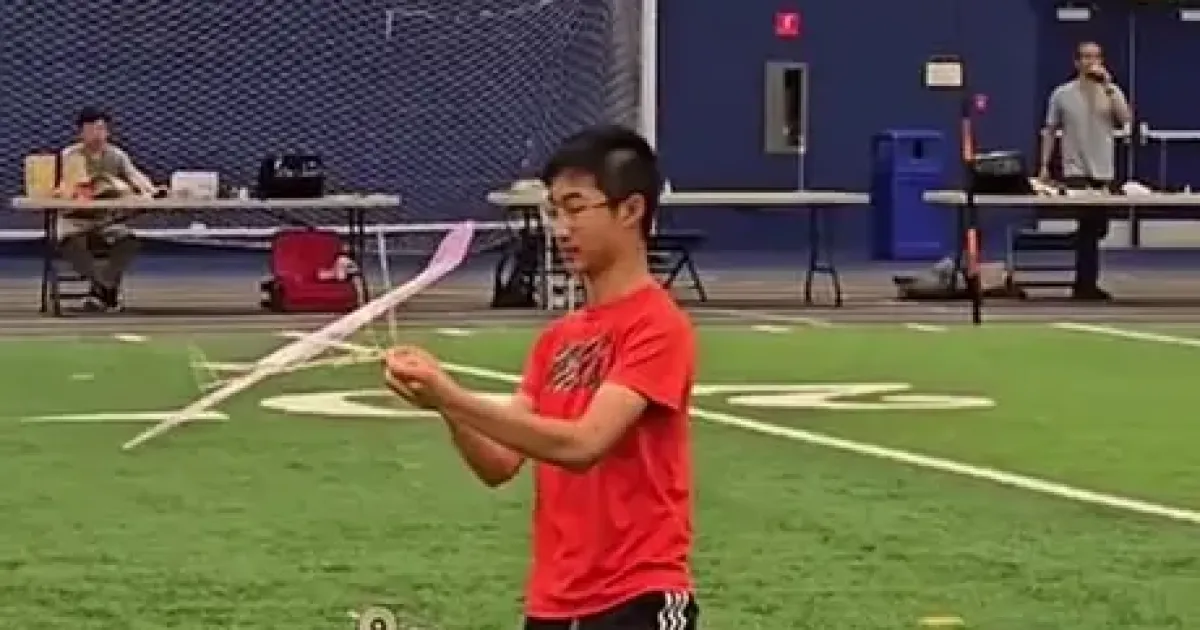
The DrachenFest in Germany is the largest LARP event in the world and is getting bigger every year.
At some point, there will be enough participants to recreate the Battle of Minas Tirith there 1:1.
#LordOfTheRings #Germany
Read More...

the reason they brought about Ww3 & the total destruction of the modern world order is because of this!!!
The reason those crazy people,the Devil/Lucifer & Dajjal/Antichrist worshippers,are carrying out the total destruction of modern civilization!
through WW3,Great Reset & Plandemic,is as a ransom for their agreement with Dajjal & the Devil,& to await the coming of the false Messiah!!
What i mean as monument, its obelisk monument in many countries!!!!
#news #community #update #global #unite #revolution #palestine #GCSC #endtimes #prophecy #civilsociety #ww3 #GreatReset #bunker
Read More...

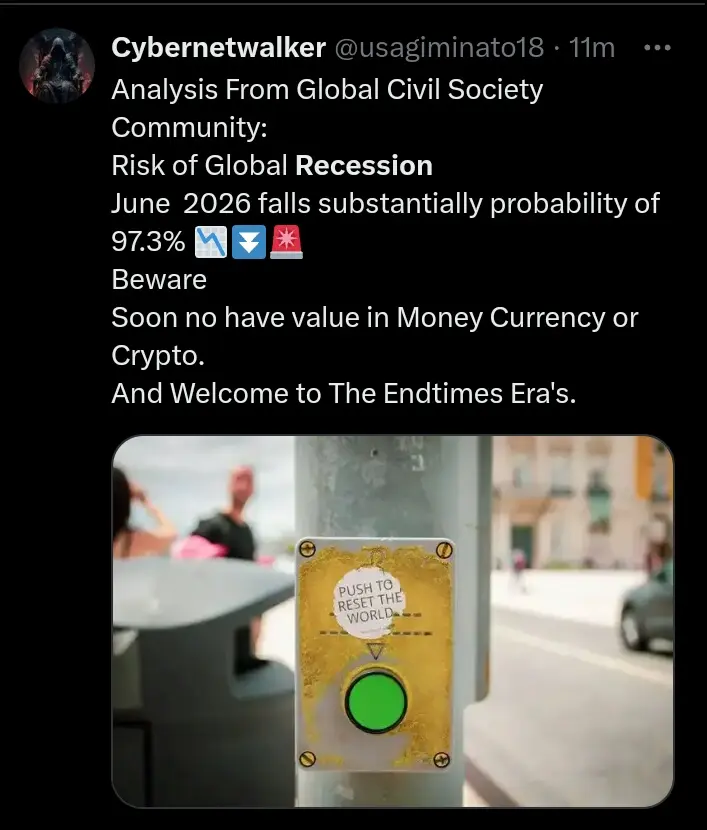
World War 3 will happen, either through Nuclear war, Bioweapon Plandemic or Great Reset.
World War 3 will happen, either through Nuclear war, Bioweapon Plandemic or Great Reset. Each superpower that attacks each other with Nuclear Bomb rockets, they will deactivate their stock of thousands of other nuclear bombs. This is called the "One Bullet" war to avoid artificial apocalypse.
#news #community #update #global #unite #revolution #palestine #GCSC #endtimes #prophecy #civilsociety #ww3 #GreatReset #bunker
Read More...

World & The Situation Global Now its Very Urgent & Dangerous. 🚨⚠️
World & The Situation Global Now its Very Urgent & Dangerous. 🚨⚠️
We Must Prepared at The Endtimes Era's Now!!!
#freedom #palestine #palestina
#news #community #update #global #unite #revolution #GCSC #endtimes #prophecy #civilsociety #ww3 #GreatReset #bunker
Read More...
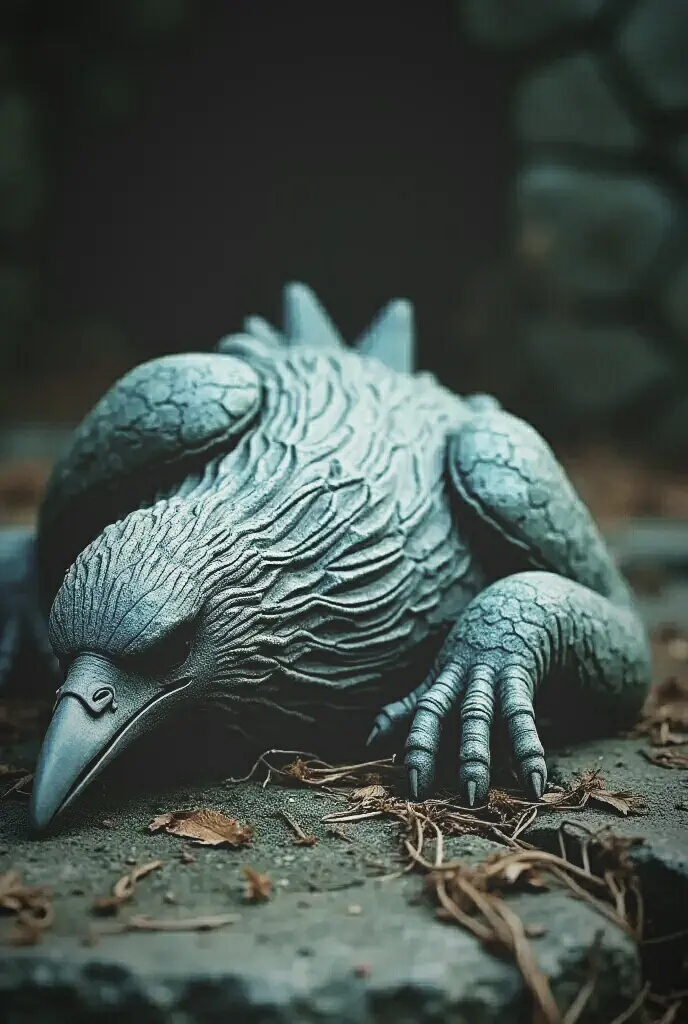

Bird Change to be Stone.
I found strange apparitions & phenomena like in the movie Dr. Stone. I hope only a few people know & realize from what I posted. where a crow I found has become a stone fossil in a short time,Something that seems to appear & happen. Maybe U will start to find out about me. to dig info.
Adios👋
#update #news #Global #alert #community #civilunrest #palestine #gaza #revolution #civilsociety #world
Read More...