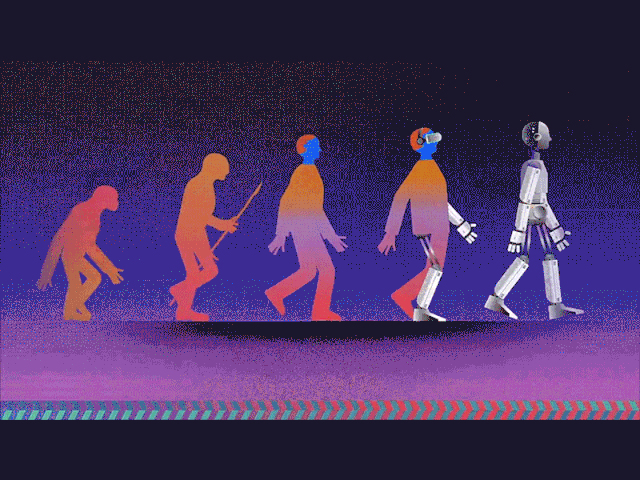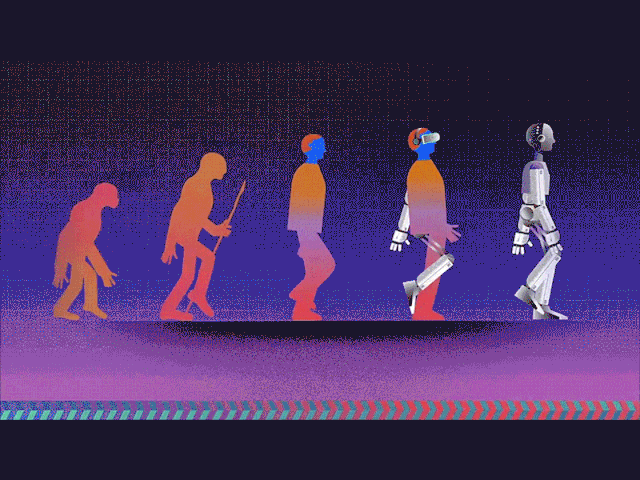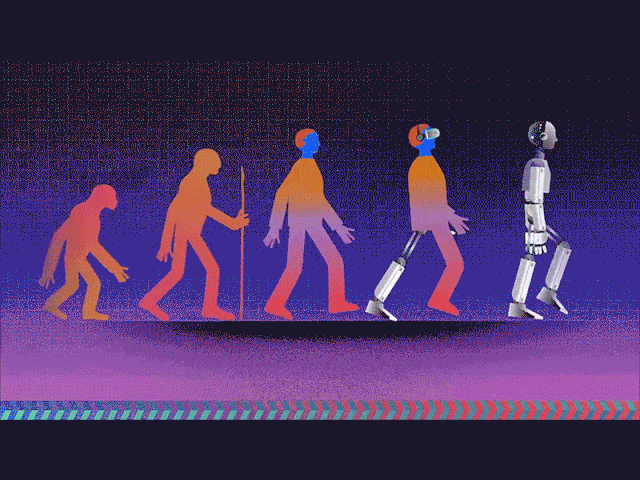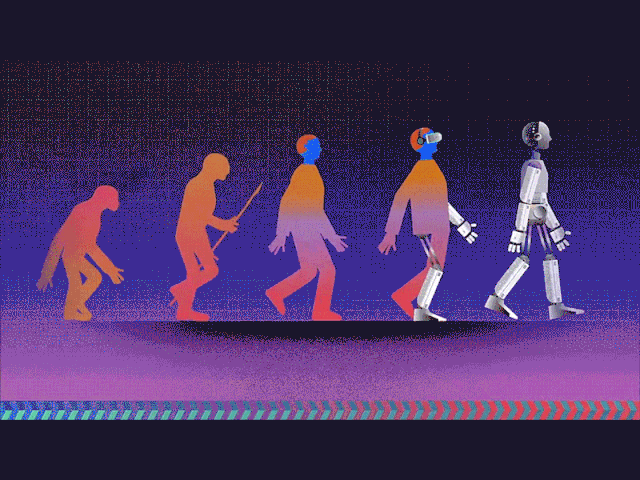The Evolution of Humanity
The story of human evolution is a fascinating journey that spans millions of years, detailing the transformation of early primates into modern humans. This evolutionary path is marked by significant milestones in physical, cognitive, and cultural development.
Early Beginnings
The journey of human evolution begins with our ancient primate ancestors. Around 7 million years ago, the first hominins, the group that includes modern humans and our closest relatives, diverged from the ancestors of chimpanzees and bonobos. These early hominins, such as Sahelanthropus tchadensis, had both ape-like and human-like characteristics.
The Australopithecines
One of the most well-known early hominins is Australopithecus afarensis, exemplified by the famous fossil "Lucy," discovered in Ethiopia. Living around 3.9 to 2.9 million years ago, Australopithecus afarensis walked upright on two legs, a crucial step in human evolution, while still retaining some tree-climbing adaptations.
The Genus Homo
Around 2.4 million years ago, the genus Homo emerged. Homo habilis, known as the "handy man," was one of the earliest members of this genus. Homo habilis is associated with the creation of simple stone tools, marking the beginning of technological innovation.
Homo Erectus and Migration
Homo erectus, appearing around 1.9 million years ago, was a significant step forward in human evolution. This species exhibited larger brain sizes and more advanced tool use. Homo erectus was also the first hominin to migrate out of Africa, spreading to Asia and Europe, showcasing adaptability and survival skills in diverse environments.
Neanderthals and Modern Humans
One of the most famous relatives of modern humans is the Neanderthal (Homo neanderthalensis), who lived in Europe and western Asia. Neanderthals were skilled hunters and toolmakers, and they even created symbolic art and buried their dead. Around 300,000 years ago, Homo sapiens, our own species, emerged in Africa. Homo sapiens exhibited advanced cognitive abilities, leading to sophisticated language, art, and cultural practices.
The Great Leap Forward
Approximately 70,000 years ago, Homo sapiens underwent a "Great Leap Forward," marked by a significant increase in creativity and technological innovation. This period saw the development of complex tools, art, and the beginnings of organized societies.
The Agricultural Revolution
About 10,000 years ago, the Agricultural Revolution transformed human societies. The domestication of plants and animals led to the development of agriculture, allowing humans to settle in one place and form complex civilizations. This period saw the rise of cities, writing systems, and advanced technologies.
Modern Humans
Today, Homo sapiens are the only surviving members of the hominin lineage. Our species has spread across the globe, adapting to various environments and developing diverse cultures. The study of human evolution continues to uncover new insights, helping us understand our origins and the traits that make us uniquely human.
The journey of human evolution is a testament to the resilience, adaptability, and ingenuity of our ancestors. It highlights the incredible transformations that have shaped us into the complex beings we are today.
1 year ago
Share
Add Comment